Key Differences:Prototype PCB Assembly vs. PCB Prototype
Arictle Summary
Comprehending the distinction between model Prototype PCB Assembly and production PCB manufacturing is crucial for anyone operating in electronics development. While both processes include producing functional printed circuit boards, they serve basically different functions in the product development lifecycle. A prototype is an early version designed for PCB assembly testing and recognition, while production PCBs are made for commercial circulation. This broad guide prototypes and production examine the significant difference between the PCB assembly, helping you make a notified option about using each technology and how to increase your PCB project from the concept to the market.
Table of Contents
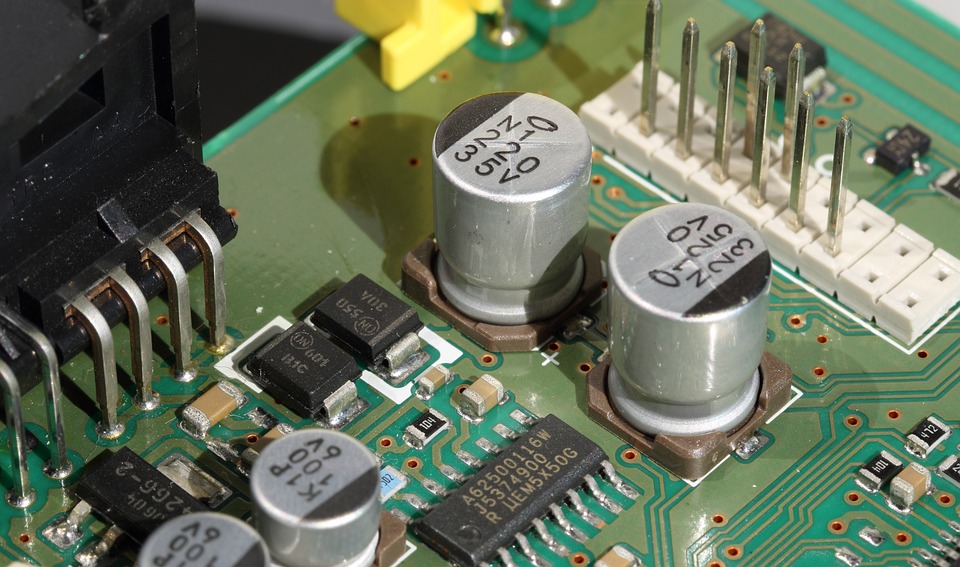
Prototype PCB assembly represents the initial phase of printed circuit board development, where engineers create small amounts of PCBs to check and confirm their board style. A Prototype PCB Assembly is a preliminary variation that allows designers to recognize possible concerns, validate functionality, and fine-tune their circuit board before devoting to mass production. Prototype PCB Assembly is a crucial action that can save substantial time and costs by catching design flaws early in the development procedure.
The pcb prototyping service generally includes quick-turn pcb fabrication, where manufacturers prioritize speed over expense effectiveness. This method makes it possible for fast iteration and screening, enabling engineers to make essential modifications to their printed circuit board style before transferring to production phases. Professional PCB manufacturers frequently specialize in prototype production, offering flexible assembly services that accommodate regular design changes and little batch requirements.
Throughout the prototyping stage, electronic elements are carefully chosen and checked to make sure compatibility with the total style. The assembly procedure for prototypes often involves more manual work and specialized attention compared to automatic assembly line. This hands-on method enables greater flexibility in element positioning and enables engineers to try out different setups to optimize their pcb board performance.
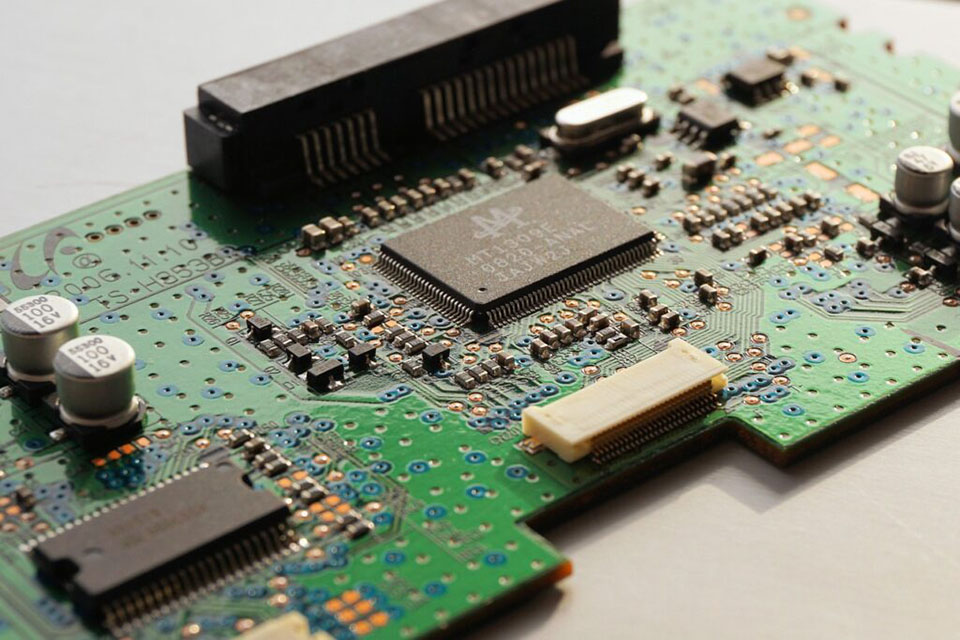
How does the production vary from PCB assembly prototype?
Production focuses on high volume production with PCB assembly stability, cost effectiveness and scalability. Prototype PCB assembly which focus on speed and flexibility, production PCB assembly is designed to achieve scale economies through standardized procedures and automatic manufacturing. The manufacturing procedure is enhanced for volume production, using production lines geared up with sophisticated pick-and-place makers and reflow ovens for consistent solder joint quality.
PCB manufacture and assembly for production includes extensive quality control systems and rigorous testing protocols to make sure reliability throughout thousands or millions of systems. Production pcb assembly manufacturers execute statistical procedure controls and automated optical inspection to preserve consistent quality requirements. The assembly to fulfill production requirements typically includes collaborations with specialized pcb factories that can manage high-volume orders efficiently.
The shift from Prototype PCB Assembly to production requires mindful planning and paperwork. Gerber files should be settled, costs of materials locked down, and assembly directions standardized. Production runs need complete pcb documentation that leaves no space for analysis, as any ambiguity can result in expensive production errors when multiplied across countless units.
What Are the Secret Differences in Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing procedures for model and production PCBs differ significantly in their approach, equipment, and optimization objectives. Model production prioritizes flexibility and quick turnaround, frequently using smaller-scale devices that can accommodate frequent setup modifications. Through-hole elements and surface install gadgets are usually placed utilizing semi-automated or manual procedures, enabling simple modifications and experimentation during the pcb advancement phase.
Production production stresses effectiveness and consistency through extremely automated systems. Modern production centers use sophisticated pick-and-place devices capable of putting countless electronic parts per hour with remarkable accuracy. The surface area of the pcb is prepared using standardized processes, and solder paste application is managed through exact stenciling techniques. Reflow ovens in production environments are calibrated for specific thermal profiles that ensure constant solder joint development across whole production batches.
Quality assurance steps likewise vary significantly between model and production processes. Prototype PCB Assembly typically counts on functional screening and visual assessment, while production assembly incorporates automated optical inspection, in-circuit screening, and analytical tasting procedures. The production and assembly services for production include detailed traceability systems that track parts, procedures, and test results for each private circuit board production batch.
How Do Lead Times Compare In Between Prototype PCB Assembly and Production PCBs?
Preparation represents among the most significant differences in between prototype and production PCB assembly. Prototype services are specifically developed for fast turnaround, with many prototyping company offering shipment within 24-48 hours for simple designs. This quick-turn technique makes it possible for engineers to iterate rapidly throughout the design recognition stage, enabling several design modifications within a brief timeframe.
Production lead times are substantially longer due to the complexity of scaling production procedures and ensuring quality consistency. Common production pcb preparation range from numerous weeks to months, depending on the intricacy of the style, part schedule, and production volume requirements. The extended timeline accounts for detailed design evaluations, tooling preparation, procedure recognition, and quality system implementation.
The difference in lead times shows the fundamental goals of each procedure. Prototype pcb assembly prioritizes speed to allow fast style iteration, while production assembly focuses on establishing robust, repeatable processes that can provide consistent quality at scale. Comprehending these preparation differences is important for job planning and making sure that advancement schedules align with market requirements and company goals.
What Cost Considerations Should You Element Into Your PCB Order?
Cost structures for prototype and production PCB assembly follow completely various designs, showing their distinct objectives and making methods. Prototype costs are generally greater on a per-unit basis due to the specialized attention, fast turn-around requirements, and smaller sized economies of scale. Nevertheless, the total financial investment for model advancement is fairly modest, making it an outstanding financial investment for style recognition and risk mitigation.
Production costs focus on achieving the most affordable possible per-unit rate through volume discount rates, automated processes, and enhanced supply chain management. While the preliminary setup expenses for production can be significant, including tooling, screening fixtures, and process recognition, these costs are amortized across big production volumes. The result is substantially lower per-unit expenses that make commercial circulation financially viable.
When planning your pcb job budget, consider the total expense of ownership consisting of development time, screening requirements, and possible redesign expenses. Buying extensive model screening can prevent costly production errors that might require pricey recalls or redesigns. The secret is stabilizing model thoroughness with time-to-market pressures while guaranteeing that production expenses line up with target item pricing and earnings margins.
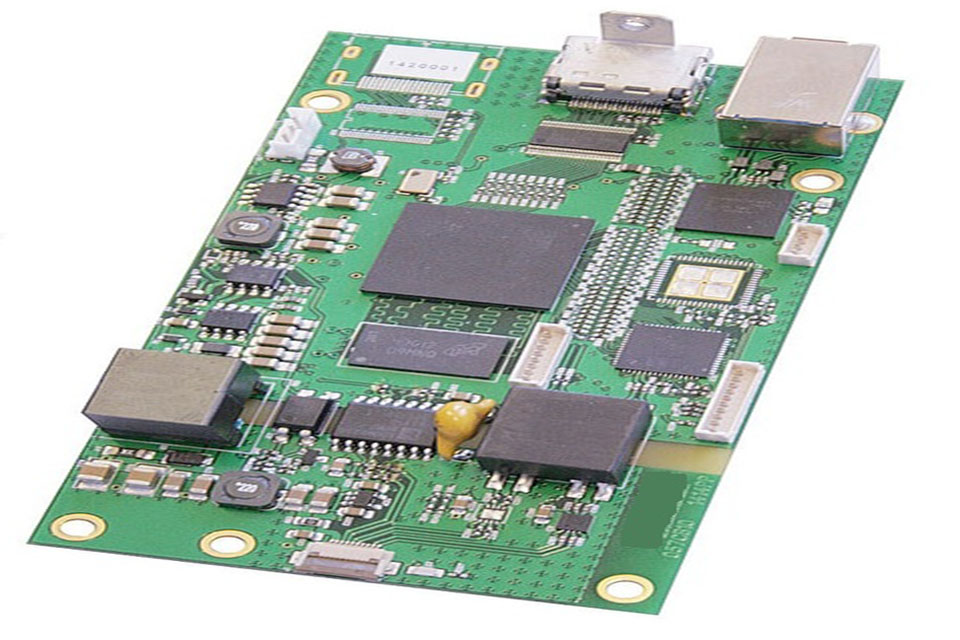
How Does PCB Design Effect Prototype PCB Assembly vs Mass Production?
PCB style factors to consider differ significantly between prototyping and mass production phases, with each requiring various optimization methods. Prototype designs frequently prioritize ease of access for screening and adjustment, integrating functions like test points, jumpers, and available part placements that help with debugging and recognition. Board style for models may include additional space for penetrating and may use larger part bundles that are simpler to work with during development.
Production focuses on PCB design manufacturing, cost adaptation and long -term reliability. Style for production (DFM) principles end up being crucial, highlighting component standardization, automated assembly compatibility, and supply chain optimization. Production designs generally reduce board size to reduce material costs, optimize part positioning for automated assembly, and include design rules that ensure constant manufacturing yields.
The shift from model to production typically requires style adjustments to accommodate manufacturing constraints and expense targets. This might involve component substitutions, layout optimizations, or style rule changes that improve manufacturability while maintaining performance. Printed circuit board design software application tools often include DFM examining features that assist determine potential production problems before committing to production.
What Quality and Dependability Standards Apply to Each Process?
Quality and reliability requirements differ significantly in between model and production PCB assembly, reflecting their intended applications and lifecycles. Model quality focuses on practical confirmation and style recognition, with testing treatments designed to recognize style flaws and verify performance under numerous operating conditions. While model screening is extensive, it usually does not consist of the comprehensive reliability testing required for industrial products.
Production PCB assembly should satisfy strict quality standards including industry accreditations, regulatory compliance, and long-lasting dependability requirements. Comprehensive pcb assembly involves several screening phases consisting of incoming evaluation, in-process screening, last practical screening, and reliability validation. Production screening protocols often consist of sped up aging tests, thermal biking, vibration screening, and other ecological tension tests that mimic years of operation.
The dependability expectations for production PCBs are substantially greater, as failures in the field can lead to expensive recalls, guarantee claims, and brand name damage. This requires implementing robust quality management systems, statistical procedure controls, and comprehensive documentation that guarantees traceability and makes it possible for constant enhancement. The assembly process for production includes multiple checkpoints and recognition steps that would be unwise for model quantities.
When Should You Choose Prototype PCBs Over Production Assembly?
The choice between prototype and production assembly depends upon your job phase, goals, and risk tolerance. Prototype PCBs are necessary throughout the initial design and recognition phases when you need to verify performance, test different element alternatives, or confirm design concepts. Prototype is an important action whenever you are developing brand-new products, executing important design modifications, or working with unknown innovations or elements.
Select prototype assembly when you require flexibility to make design adjustments, when you’re conducting performance testing or regulatory compliance screening, or when you’re developing proof-of-concept presentations for financiers or customers. Little batch model production is also important for restricted market testing, beta programs, or custom-made applications where production volumes don’t validate major manufacturing setup.
Production assembly ends up being proper when your design is settled, tested, and prepared for business circulation. This transition point typically occurs after successful model recognition, regulative approval, and market recognition. The choice to move to production ought to think about not only technical preparedness however likewise market need, supply chain stability, and company objectives consisting of prices and success targets.
How Do PCB Manufacturers Handle Different Order Volumes?
PCB makers typically specialize in either model or production volumes, with various facilities, devices, and processes optimized for each market section. Prototype pcb assembly services concentrate on flexibility, quick turn-around, and engineering support, often preserving smaller production lines that can accommodate frequent setup modifications and customized requirements. These facilities generally handle orders ranging from single units to numerous pieces.
Production pcb assembly producers are equipped for high volume orders, generally beginning at thousands of units and scaling to millions. These centers invest in high-speed automated devices, extensive quality systems, and supply chain partnerships that support massive production. The minimum order quantities for production assembly reflect the setup expenses and process validation requirements connected with production-scale operations.
Numerous detailed pcb solutions companies provide both model and production services, allowing seamless transitions from advancement to manufacturing. This method supplies continuity in design understanding, process understanding, and quality standards. However, some business choose to deal with specialized providers for each phase, optimizing for the specific requirements and abilities required for prototype versus production stages.
What Are the Best Practices for Transitioning from Prototype to Production?
Effectively transitioning from model to production needs careful preparation, documentation, and recognition to ensure that production PCBs preserve the performance and performance demonstrated in models. Begin by carrying out extensive prototype screening that verifies not just standard functionality but likewise efficiency under various ecological and tension conditions. This screening must recognize any potential dependability issues that could affect production yields or field performance.
Document all style choices, part choices, and assembly requirements that were confirmed throughout the prototype phase. Develop comprehensive assembly drawings, pick-and-place files, and test procedures that catch the understanding gotten throughout prototype advancement. Gerber files need to be examined and enhanced for production manufacturing, incorporating any style improvements identified during prototype testing while ensuring compatibility with production devices and processes.
Confirm the production process through pilot runs that bridge the gap between model and complete production. These pilot runs enable you to determine and deal with any making concerns before dedicating to big production volumes. Work closely with your pcb assembly maker to enhance the production process, verify quality treatments, and establish the supply chain collaborations needed for effective volume production. This collaboration ensures that the transition from prototyping and production keeps design stability while achieving the cost and quality goals required for industrial success.
Secret Takeaways: Essential Points to Keep In Mind
- Prototype PCB assembly prioritizes speed and versatility – designed for fast model, screening, and design recognition with fast turnaround times typically determined in days rather than weeks
- Production assembly concentrates on volume, consistency, and cost effectiveness – optimized for high-volume manufacturing with automated procedures and economies of scale
- Preparations differ significantly – models can be delivered in 24-48 hours while production orders typically need weeks to months for completion
- Cost structures are basically various – models have greater per-unit costs but lower total financial investment, while production accomplishes lower per-unit costs through volume
- Quality requirements escalate significantly in production – production PCBs must fulfill stringent reliability standards, regulative compliance, and long-term efficiency requirements
- Design factors to consider change in between stages – model styles prioritize testability and adjustment capability while production styles focus on manufacturability and expense optimization
- Pick models for style recognition and testing – vital for validating functionality, identifying concerns, and refining designs before production dedication
- Shift planning is essential for success – detailed documentation, procedure validation, and pilot runs guarantee effective scaling from prototype to production
- Manufacturer expertise affects service quality – model specialists excel at versatility and speed while production professionals enhance for volume and consistency
- Investment in thorough prototyping prevents pricey production errors – identifying possible concerns throughout prototyping is a vital action that can conserve significant time and costs in the long term