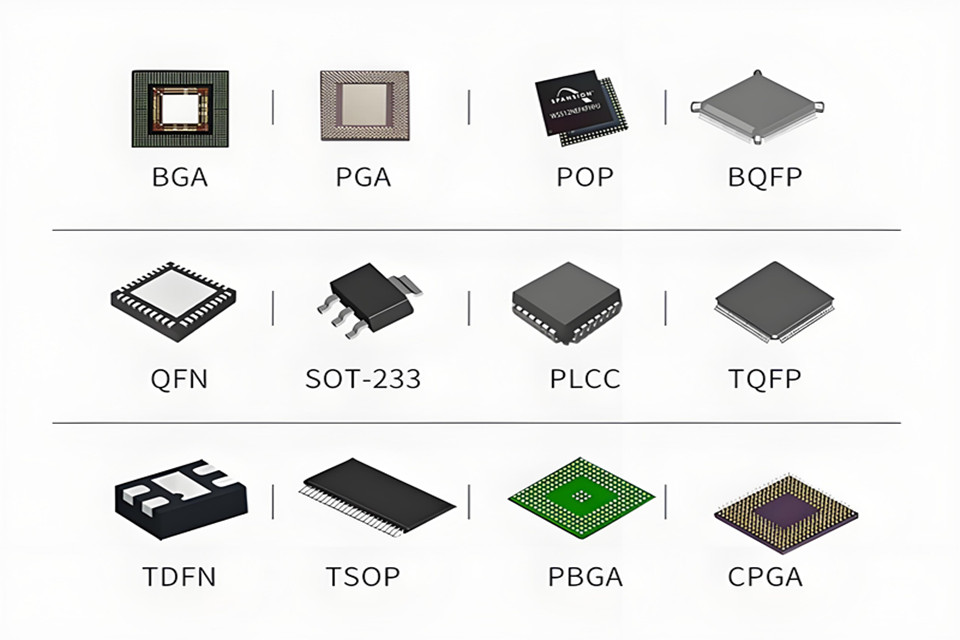
BGA vs. QFP vs. QFP
Odată cu dezvoltarea rapidă a tehnologiei electronice, tehnologia de ambalare a cipurilor, ca legătură centrală între dispozitivele semiconductoare și plăcile de circuit, afectează direct performanța, fiabilitatea și costul echipamentelor. BGA (Matrice de grilă cu bile), QFP (Pachet Quad Flat) şi LGA (Land Grid Array) există trei forme principale de ambalare, care satisfac diverse nevoi de aplicare prin structuri fizice și caracteristici de proces diferite.
- Ambalaj BGA este cunoscut pentru matricea sa de bile de lipit de înaltă densitate. Datorită performanței sale excelente de înaltă frecvență și capacităților de disipare a căldurii, a devenit alegerea principală pentru calculul de înaltă performanță, comunicațiile 5G și dispozitivele mobile;
- Ambalaj QFP se bazează pe un design cu patru pini și este utilizat pe scară largă în electronica de larg consum și în scenarii generale, datorită costului redus și avantajelor de detectare ușoară;
- Ambalaj LGA obține o fiabilitate mai mare printr-o matrice de contacte conectabile, în special în domeniul procesoarelor desktop și al controlului industrial.
Cuprins
Acest articol va analiza în profunzime principiile, avantajele și dezavantajele, precum și scenariile tipice de aplicare ale acestor trei tehnologii de ambalare, pentru a ajuta inginerii și dezvoltatorii să facă cea mai bună alegere în funcție de nevoile reale.
Rezumatul articolului
- Pachet BGA
- CaracteristiciAdoptă o matrice de bile de lipit inferioare pentru a oferi densitate mare de I/O (numărul de pini poate ajunge la sute sau chiar mii), întârziere mică în transmiterea semnalului, eficiență ridicată de disipare a căldurii, iar volumul este redus cu peste 50% în comparație cu capsulele tradiționale.
- AvantajePerformanță excelentă la frecvență înaltă, stabilitate mecanică puternică, potrivită pentru scenarii cu integrare ridicată (cum ar fi cipuri de server, procesoare pentru smartphone-uri).
- DezavantajeNu poate fi înlocuit după sudare, necesită inspecție cu raze X și are costuri ridicate de refacere.
- Pachet QFP
- CaracteristiciAranjament cu patru laturi al pinilor, proces matur, cost redus, potrivit pentru aplicații cu densitate medie și mică.
- AvantajeDetectare intuitivă, suportă montare la suprafață SMT, potrivită pentru domenii electronice generale, cum ar fi senzori și dispozitive de consum redus de energie.
- DezavantajeSpațierea mică între pini duce la parametri paraziți ridicați, capacitate slabă de disipare a căldurii și performanță limitată la frecvență înaltă.
- Pachet LGA
- CaracteristiciSe conectează la mufa plăcii de bază prin contactul inferior, acceptă un design conectabil și are o fiabilitate ridicată.
- AvantajeCapacități puternice de gestionare termică, instalare ușoară, stabilitate bună pe termen lung, utilizat pe scară largă în procesoarele desktop (cum ar fi seria Intel LGA) și în sistemele de control industrial.
- DezavantajeDimensiuni mari, necesită prize suplimentare și cost ridicat.
Rezumat:
- BGA este potrivit pentru scenarii cu cerințe stricte de performanță (cum ar fi calcul de înaltă performanță, module de comunicare);
- QFP este prima alegere pentru aplicații de uz general, cu costuri reduse (cum ar fi electronica de larg consum);
- Agenția Locală de Apel are performanțe bune în domenii care necesită upgrade și stabilitate (cum ar fi procesoarele desktop).
Comparând performanța electrică, managementul termic, costul și mentenanța celor trei, inginerii pot alege în mod flexibil soluții de ambalare în funcție de cerințele produsului pentru a echilibra performanța, costul și fiabilitatea.
Următorul este un tabel comparativ al performanței între Pachet BGA şi Pachet QFP
Comparație de performanță BGA vs. QFP
| Dimensiuni de comparație | Pachet BGA | Pachet QFP |
|---|---|---|
| Densitatea I/O | Densitate mare de I/O, configurația matricei de bile de lipit, numărul de pini depășește cu mult QFP | Număr mediu de pini, aranjament pe patru laturi, potrivit pentru aplicații cu densitate medie și mică |
| Performanța electrică | Întârziere mică a transmisiei semnalului, traseu scurt al bilei de lipit, zgomot redus, performanță excelentă de înaltă frecvență | Parametri parazitari ridicați, pini lungi, performanță limitată la frecvență înaltă |
| Management termic | Eficiență ridicată de disipare a căldurii, suprafață mare de contact a bilelor de lipit, conductivitate termică excelentă | Capacitate generală de disipare a căldurii, în funcție de pini și materialele de ambalare, rezistență termică ridicată |
| Fiabilitate | Sudare coplanară, conexiune stabilă cu bilă de lipit, rezistență puternică la solicitări mecanice | Pinii sunt ușor de rupt, sensibil la solicitări mecanice, fiabilitate redusă pe termen lung |
| Dimensiuni și greutate | Dimensiune mică, grosimea este cu 50% mai mică decât cea a QFP, economisind spațiu pe PCB | Suprafață mare, pini expuși, potriviți pentru aplicații cu spațiu liber |
| Costul de fabricație | Cost ridicat de fabricație, echipamente și procese de înaltă precizie necesare | Cost scăzut, proces simplu, potrivit pentru produse de gamă medie și inferioară |
| Detectare și reparare | Detectare dificilă, Necesită detectare cu raze X, echipament profesional necesar pentru refacere | Detectare intuitivă, calitatea sudării poate fi verificată cu ochiul liber, prelucrarea este relativ simplă |
| Scenarii de aplicare | Scenarii de înaltă performanțăCPU, GPU, cipuri de server, module de comunicare 5G | Scenarii generalesenzori, electronică de larg consum, dispozitive de consum redus |
| Complexitatea procesului | Producție automatizată, potrivit pentru producția la scară largă | Sudura manuală este fezabilă, potrivit pentru loturi mici sau dezvoltarea de prototipuri |
| Potrivirea expansiunii termice | Optimizarea potrivirii termice, reducând riscul de oboseală a îmbinărilor de lipit | Diferență mare de dilatare termică, ușor de cauzat defectarea ambalajului din cauza diferenței de temperatură |
Următorul este un tabel comparativ al performanței Pachet BGA şi Pachet LGA,
Comparație de performanță BGA vs. LGA
| Dimensiunea de comparație | Pachet BGA | Pachet LGA |
|---|---|---|
| Metoda de conectare | Matrice de bile, lipită pe PCB prin bilele de lipire inferioare | Matrice de plăcuțe, contactând direct pinii plăcii de bază prin plăcuțele metalice inferioare |
| Înlocuibilitate | Neînlocuibil, dificil de dezasamblat după lipire (necesită operațiune distructivă) | Înlocuibil, acceptă designul plug-in (necesită soclu) |
| Performanța de disipare a căldurii | Eficiență ridicată de disipare a căldurii, bilele de lipit intră în contact direct cu PCB-ul, cale scurtă de conducere a căldurii | Performanță bună de disipare a căldurii, depinde de aria de contact dintre pinii și plăcuțele plăcii de bază |
| Performanța electrică | Întârziere mică a transmisiei semnalului, traseu scurt al bilei de lipit, performanță excelentă de înaltă frecvență | Parametri parazitari scăzuti, stabilitate puternică a semnalului, potrivită pentru aplicații de înaltă frecvență |
| Volum și densitate | Volum minim, potrivit pentru integrare de înaltă densitate (cum ar fi dispozitive mobile, cipuri de server) | Volum puțin mai mare, pinii ocupă mai mult spațiu |
| Costul de fabricație | Cost scăzut, proces de sudare automatizat matur, potrivit pentru producția la scară largă | Cost ridicat, sunt necesare echipamente de sudură de înaltă precizie și prize |
| Procesul de sudare | Sudare coplanară, este necesar echipament de înaltă precizie, calitatea sudării este controlată de temperatură | Sudare prin conectare, conexiunea se realizează prin prize, iar procesul de sudare este mai stabil |
| Fiabilitate | Fiabilitate ridicată, conexiune stabilă cu bilă de lipit, rezistență puternică la solicitări mecanice | Fiabilitate ridicată, suprafață mare de contact între pini și plăcuțe, stabilitate bună pe termen lung |
| Rata de finalizare | Rată scăzută de finalizare, abaterea de la sudură duce ușor la resturi | Rată mare de finalizare, o calitate a sudurii mai controlabilă |
| Scenarii de aplicare | Scenarii de înaltă performanțăCPU, GPU, modul de comunicare 5G, cip de server | Scenarii actualizabileCPU pentru desktop, control industrial, echipamente electronice care trebuie înlocuite frecvent |
| Potrivirea expansiunii termice | Optimizarea potrivirii termice, reduc riscul de oboseală a îmbinărilor de lipit | Diferență mare de dilatare termică, este necesară o compensație materială suplimentară |
| Detectare și reparare | Detectare dificilă, este necesară detectarea cu raze X și este nevoie de echipament profesional pentru reluare | Inspecția este intuitivă, calitatea sudării poate fi verificată vizual, iar prelucrarea este relativ simplă |
Domenii tipice de aplicare
- Ambalaj BGA: –Dispozitive mobileSmartphone-uri, procesoare/procesoare grafice pentru laptopuri
- ServerCipuri de calcul de înaltă performanță, controlere de stocare
- Comunicații 5GModule RF de înaltă frecvență, cipuri pentru stații de bază
- Ambalaj LGA:
- PC desktopCPU actualizabil (cum ar fi Intel LGA 1700)
- Control industrialSisteme integrate care trebuie înlocuite frecvent
- Piață DIYDesignul plăcii de bază care permite înlocuirea de către utilizator
Rezumat comparativ al ambalajelor BGA, QFP, LGA
Ambalaj BGA (Matrice de grilă cu bile) utilizări matrice de bile de lipit a realiza densitate mare de I/O şi performanță de înaltă frecvență, care este potrivit pentru scenarii de înaltă performanță (cum ar fi CPU, GPU, module de comunicare 5G), dar are dezavantajele că neînlocuibil şi dificil de detectat; Ambalaj QFP (Pachet Quad Flat) adoptă o știft cu patru laturi design, care este ieftin și intuitiv de detectat, dar are parametri paraziți ridicați şi management termic slab, și este potrivit pentru electronică de larg consum (cum ar fi senzori și dispozitive de consum redus de energie); Pachet LGA (Matrice de grilă terestră) contactează pinii plăcii de bază printr-un matrice de plăcuțe, susține înlocuibilitate şi fiabilitate ridicatăși este frecvent utilizat în procesoare desktop şi control industrial, dar este de dimensiuni mari şi cost ridicat.