20 de factori cheie care afectează prețul PCB
Introducere
Cel/Cea/Cei/Cele pcb price is affected by a variety of aspects covering products, layout, production, quality assurance, supply chain, and market dynamics. Below is a comprehensive listing of 20 crucial factors, each explained thoroughly:
Cuprins

I. Core Board Specs affect pcb price
These are the most essential physical characteristics of the board.
1. pcb board size (Dimension) .
- Why it matters: Larger boards make use of even more basic material (laminate). Producers procedure boards on standard-sized panels; the amount of your boards fit onto one of these panels (panelization) directly effects waste and effectiveness.
- Rate Influence: Bigger board = Greater rate.
2. Variety of Layers .
- Why it matters: This is one of the most significant pcb price chauffeurs. A single-sided board is easy. A double-sided board needs a lot more actions. A multi-layer board (4, 6, 8+ layers) involves intricate lamination, pressing, and drilling processes for every extra layer.
- Price Impact: Even more layers = Considerably higher rate.
3. Base Product Type .
- Why it matters: The basic product is FR-4 (a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate), which is one of the most cost-efficient. High-frequency applications need customized products like Rogers, Teflon, sau polyimide, which are far more costly and can be more difficult to collaborate with.
- Cost Impact: Standard FR-4 = Reduced price. High-frequency/high-temperature materials = Much greater rate.
4. Board Density .
- Why it matters: Standard densities (e.g., 1.6 mm) prevail and economical. Non-standard densities, whether extremely slim or really thick, call for special product supply and may need modifications to making equipment, enhancing the cost.
- Cost Effect: Non-standard thickness = Higher cost.
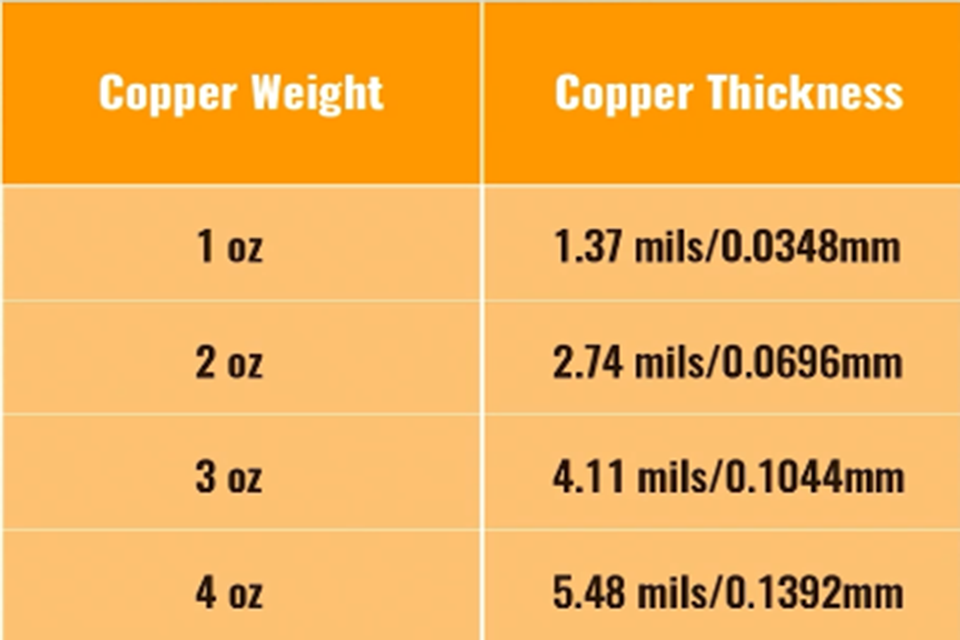
5. Copper Weight/Thickness .
- Why it matters: Standard copper weight is 1 oz (35 µm). “Heavy copper” (2 oz, 3 oz, or more) is required for high-power applications. It requires even more etching time and precision, and the raw material is much more costly.
- Rate Effect: Larger copper weight = Higher price.
II. Layout Intricacy & Precision affect pcb price
These elements associate with the problem and precision needed to make the design.
6. Minimum Trace Size and Spacing .
- Why it matters: The smaller sized the gap in between traces and the thinner the traces themselves, the greater the precision required. This requires more advanced imaging and etching tools and brings about a higher potential for defects (reduced yield), driving up the price.
- Price Effect: Tighter trace/spacing (< 5 mil) = Significantly greater cost.
7. Hole Dimension and Thickness .
- Why it matters: Drilling is a lengthy process. A a great deal of openings raises maker time. Extremely tiny mechanical drill dimensions (< 0.2 mm) are vulnerable, break more often, and need slower drilling speeds.
- Cost Impact: Extra openings and smaller sized opening sizes = Higher price.
8. Via Technology .
- Why it matters: .
- Through-hole vias: Criterion and most inexpensive (undergo all layers).
- Blind Vias: Connect an external layer to an inner layer (do not copulate with).
- Buried Vias: Attach two internal layers (not visible from the outdoors).
- Blind and hidden vias need multiple, sequential lamination and boring steps, considerably raising complexity and expense. Microvias (laser-drilled) add a lot more.
- Price Impact: Blind/buried vias = Dramatically higher rate.
- back drill :this is a special drill technology which affect pcb price as well
9. Surface Complete .
- Why it matters: The surface finish safeguards the subjected copper pads from oxidation and offers a solderable surface area.
- HASL (Hot Air Solder Progressing): Least expensive and most typical.
- Lead-Free HASL: Somewhat much more pricey.
- ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold): More costly, but flat and helpful for fine-pitch elements and BGAs.
- Immersion Silver/Tin, OSP: Other alternatives with varying prices.
- Cost Impact: HASL = Most affordable cost. ENIG/other finishes = Greater cost.
10. Impedance Control .
- Why it matters: High-speed designs call for traces to have a specific resistance (e.g., 50 ohms). This needs the producer to thoroughly regulate trace width, layer stack-up, and product. It involves extra modeling, testing (utilizing a TDR), and tighter procedure controls, every one of which include cost.
- Price Effect: Called for resistance control = Higher cost.
III. Appearance & Unique Procedures affect pcb price
11. Solder Mask Color .
- Why it matters: Eco-friendly is the universal requirement and is produced in the largest sets. Other shades like red, blue, black, or white are run much less regularly and may need a different manufacturing run and different chemistry, including a tiny cost.
- Rate Influence: Green = Least expensive cost. Other colors = Slightly greater price.
12. Silkscreen Color and Sides .
- Why it matters: A single-sided silkscreen in typical white is most affordable. Adding a silkscreen to the 2nd side enhances processing time. Using non-standard colors adds expense, similar to solder mask.
- Rate Effect: Two-sided or non-standard color silkscreen = A little greater rate.
13. Special Functions .
- Why it matters: Any type of inconsistency from a common board adds process steps. Instances consist of:.
- Gold Fingers: For edge adapters, calls for extra plating steps.
- Castellated Holes: Layered holes on the side of the board.
- Carbon Ink: For button contacts.
- Via-in-Pad: Needs a special procedure to fill up the by means of and plate over it.
- Rate Impact: Any unique feature = Higher cost.
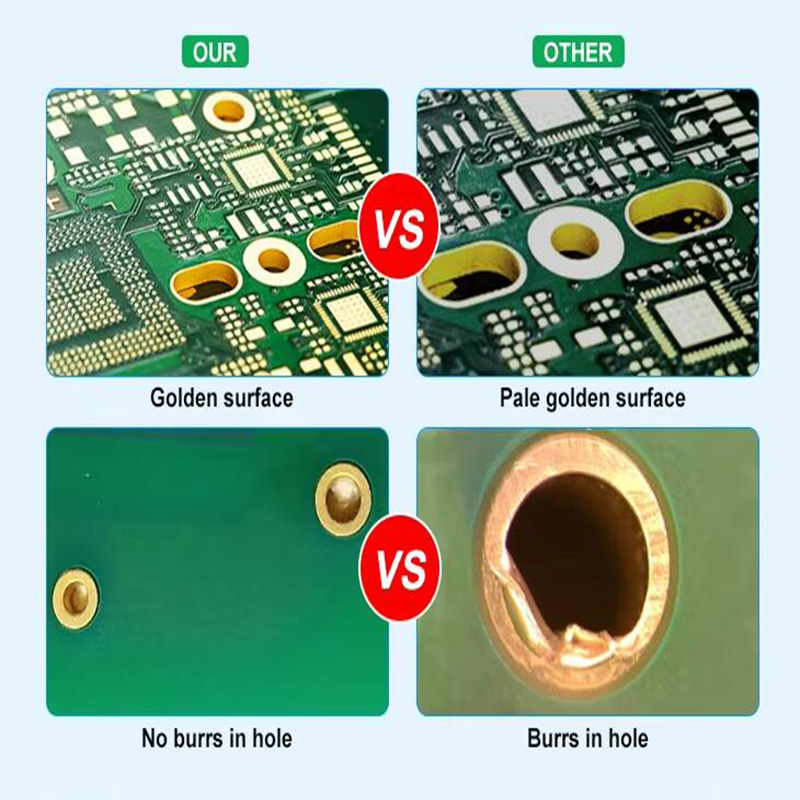
IV. Order Logistics & Volume affect pcb price
14. Order Amount .
- Why it matters: Economic situation of scale is huge in PCB production. The initial arrangement cost (tooling, equipment programs) is the same whether you buy 5 boards or 5,000. This arrangement price is amortized over the amount, so the per-board price declines dramatically with greater volumes.
- Rate Effect: Higher quantity = Much reduced cost per board.
15. Turnaround Time (Preparation) .
- Why it matters: Common preparations (e.g., 2-3 weeks) enable the producer to effectively schedule your task with others. An accelerated or quick-turn order needs them to disrupt their schedule, devote resources, and in some cases run devices inefficiently, which lugs a substantial premium.
- Cost Influence: Faster turnaround = Substantially greater cost.
16. Panelization Demands .
- Why it matters: If you have specific requirements for how your boards are panelized (e.g., with V-grooves vs. tab-routing, or particular positioning of tooling strips), it can influence exactly how efficiently the manufacturer utilizes their master panel, possibly boosting waste and expense.
- Rate Effect: Complex/inefficient panelization = Greater price.
V. High Quality, Testing & Conformity affect pcb price
17. Electric Checking .
- Why it matters: All reliable suppliers perform electric testing on production boards to check for shorts and opens up.
- Flying Probe Examination: Ideal for prototypes and tiny quantities. A machine probes every internet. No personalized component is needed, however it’s slow.
- Bed of Nails (Component) Examination: For high quantities. A personalized component is constructed to evaluate all nets simultaneously. The component is expensive, but the per-board screening time is seconds.
- Price Impact: The price is factored in; flying probe for little quantity, component cost for huge volume. Missing it (not suggested) would certainly be less expensive however high-risk.
18. IPC Class Requirements .
- Why it matters: IPC requirements define top quality levels.
- IPC Course 2: Requirement for many industrial electronic devices.
- IPC Course 3: Stricter criterion for high-reliability applications like clinical, aerospace, and armed forces. It calls for tighter tolerances, even more comprehensive inspection, and higher-quality materials.
- Price Impact: IPC Class 3 = Significantly greater price.
19. Qualifications (e.g., UL, RoHS) .
- Why it matters: Calling for a board to be UL accredited (for flammability/safety) or RoHS compliant (lead-free) means the manufacturer must make use of qualified materials and processes, which can be somewhat extra costly.
- Price Effect: Specific qualifications = Somewhat higher price.
20. Maker and Place .
- Why it matters: A supplier in an area with reduced labor and overhead costs (e.g., China) will generally use reduced rates than one in a region with greater costs (e.g., The United States and Canada, Europe). However, this can be balanced out by shipping expenses, import tariffs, interaction challenges, and longer lead times.
- Rate Influence: Domestic/Western manufacturing = Greater cost. Abroad manufacturing = Reduced cost (yet take into consideration overall cost).
6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the biggest factor that increases the pcb price ?
The number of layers is one of the most important cost drivers. 2-4, 6, or 8-layer boards require several complex tearing and drilling cycles to go from the board, dramatically increases the capacity for manufacturing time, materials and errors, all of which increase the price to a large extent.
How can I reduce prototype pcb price ?
To save money on the prototype, stick to the manufacturer’s standard specifications. This usually means: a 2-layer board, standard thickness (1.6 mm), 1 ounce copper weight, liberal trace/vacancy (> 6 mi), a green mixing mask, and the cheapest hall surface. Most importantly, choose a long, non-expedited lead time.
Why is the per pcb price board so high for small amounts?
PCB manufacturing includes a fixed “tooling” or setup cost for every unique design. This cost is the same whether you order 5 boards or 500. On a small run, this setup fee spreads to low boards, which makes a very high price price. As the quantity increases, this cost is refinement, the price per board decreases significantly.
What is the cheapest surface finish for a PCB?
HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) is usually the cheapest and most common surface finish available. Although it is excellent for the use of common-manual, it may not be suitable for very fine pitch components. The next cheapest option is usually OSP (organic solderability preservatives) or immersion tin.
Does the color of the solder mask actually affect the pcb price?
Yes, but usually only a little. The green industry is the standard and is produced in the largest batches, making it the most cost -effective option. Request other colors like black, red, blue,
Why does a “quick-turn” or expedited order cost so much more?
A standard lead time allows the manufacturer to efficiently group your order with others. A quick-turn order forces them to interrupt this schedule, dedicate a production line to your job, and expedite every process. You are paying a premium for this priority service that disrupts their standard workflow.
Rezumat
By thinking about all these aspects, you can better understand and prepare for the pricing structure of PCB-uri for different applications and industries. Each variable can communicate with others, and the last price is usually the outcome of a complex interaction between style needs, producing capacities, top quality standards, and market forces.