8 Estrategias clave para placas de circuito impreso para crear productos perfectos
Abstracto
In the fiercely competitive electronic manufacturing industry like PCB board production , “zero defect” has evolved from an ideal goal to a survival criterion. This article uses 8 systematic strategies, combined with industry certification standards, advanced testing technologies and supply chain management practices, to provide electronic manufacturing companies with a full-process solution from design to after-sales. The article specifically introduces authoritative tools such as SiliconExpert, and through case analysis and expert advice, helps manufacturers break through quality bottlenecks and achieve a dual improvement in product reliability and market competitiveness.
Tabla de contenido
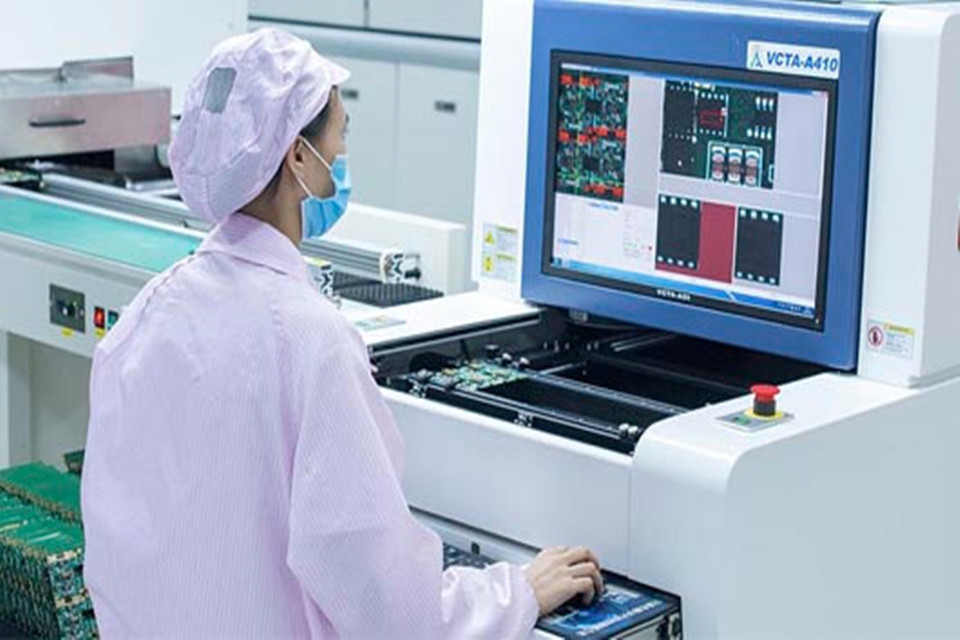
Core pcb baoard strategy 1: Intelligent test system construction
Test technology matrix upgrade
- In-circuit test (ICT): 99.5% defect coverage achieved through flying probes
- Automatic optical inspection (AOI): 18% higher defect recognition rate than traditional visual inspection
- Functional test (FCT): Simulate real application scenarios to verify system stability
Caso: Foxconn reduced the motherboard defect rate from 0.3% to 0.05% by deploying AOI+X-ray inspection system

Test frequency optimization model
| Tipo de producto | Initial test frequency | Stable test frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Electrónica de consumo | 100% full inspection | Random inspection by batch (5%-10%) |
| Equipo médico | 100% full inspection | Random inspection of 1 piece for every 500 pieces |
| Aeroespacial | 100% full inspection | Random inspection of 1 piece for every 100 pieces |
Estrategia de la placa base pcb principal 2: Sistema de certificación y evaluación de proveedores
Lista de certificación clave
- ISO 9001: Basic quality management system
- ISO 13485: Medical device-specific standard
- AS9100: Aerospace industry specification
- IECQ QC 080000: Hazardous substances process management
Supplier evaluation dimensions:
- Capacidades técnicas: Experience ratio of Class 2/Class 3 electronic products
- Equipment level: Calibration equipment coverage (recommended ≥95%)
- Audit records: Annual internal audit times (≥4 times)
- Emergency response: 48-hour defect feedback mechanism
Estrategia central de la placa pcb Tres: Control de calidad de la cadena de suministro
Tecnología de detección contra la falsificación
- XRF spectral analysis: Identify metal components
- Laser coding verification: IC chip unique identification tracking
- Blockchain traceability: Establish an unalterable supply chain archive
Estrategia de control de costos:
- Adopt the “quality cost curve” model
- Establish a “red, yellow, green” hierarchical procurement system
Estrategia central de la placa pcb Cuatro: Optimización del diseño para la fabricabilidad
Aplicación de los principios de DFM
- PCB layout: Pad spacing ≥ 0.2mm (IPC-7351 standard)
- Component selection: JEP106 certified devices are preferred
- Process compatibility: SMT reflow temperature curve optimization
Estrategia central de la placa pcb Cinco: Gestión de proyectos de alta complejidad
Modelo de Madurez del Proyecto
| Phase | Key Indicators |
|---|---|
| Concept Phase | FMEA Completion 100% |
| Development Phase | DFMEA Coverage ≥ 85% |
| Mass Production Phase | PPAP Document Completeness 100% |
Expert Advice:
- Medical device manufacturers need to ensure that suppliers have ISO 14971 risk management capabilities
- Avionics projects are recommended to adopt the DO-254 standard verification process
Estrategia central de la placa pcb Seis: Soporte de servicio de ciclo de vida completo
Módulo Funcional del Sistema PLM
- Requirement Management: Tracking Customer Change Requests
- Change control: ECN (engineering change notification) automation
- Document management: Comply with 21 CFR Part 11 regulations
Caso: Siemens shortened product iteration cycle by 40% through Teamcenter PLM system
Estrategia central de la placa pcb 7: Estandarización del proceso de fabricación
Tabla de parámetros de control de proceso
| Proceso | Control range | Inspection frequency |
|---|---|---|
| SMT printing | Solder paste thickness 200±25μm | 3 times per shift |
| Soldadura por reflujo | Peak temperature 245±5℃ | 1 time per hour |
| Soldadura por ola | Preheating temperature 110±10℃ | Each production batch |
Advanced equipment recommendation:
- [DEK printer]
- [MARCH reflow oven]
Placa base pcb principal Estrategia 8: Construcción del sistema de garantía postventa
Proceso de análisis de fallos
- Data collection: EDAC system collects on-site failure data
- Root analysis: FMEA+8D method locates problems
- Continuous improvement: CAPA (corrective and preventive action) tracking
Service commitment:
- Medical equipment provides a 5-year warranty
- Industrial control products promise 72-hour on-site response
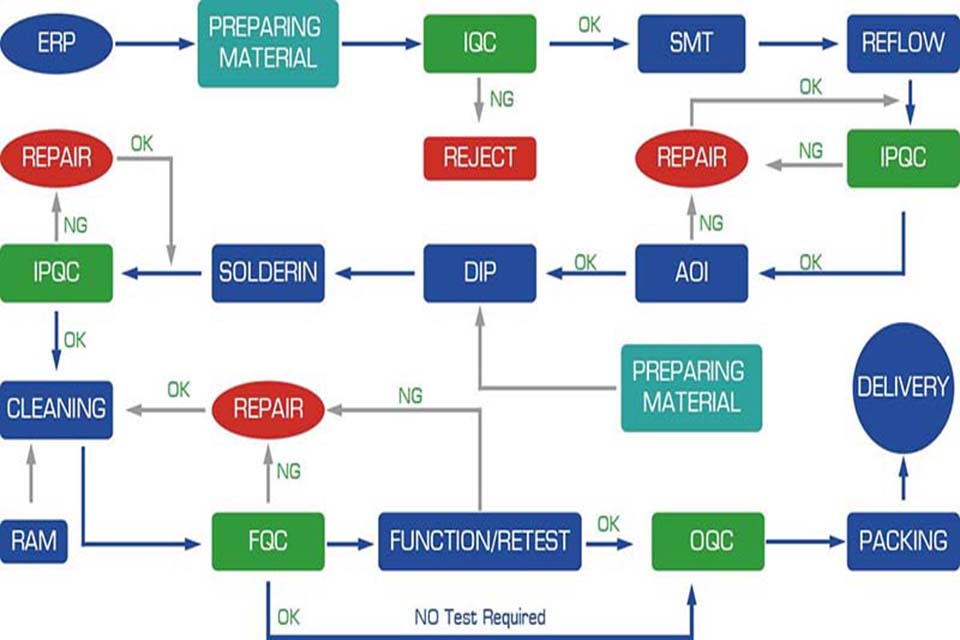
FAQ: Preguntas frecuentes sobre la implementación de cero defectos
How to choose a suitable EMS supplier?
Use the “3C” evaluation method: Certification, Capability, Case Study. It is recommended to give priority to suppliers with J-STD-001 certification.
How does the test frequency balance cost and quality?
Apply the “cost-quality balance model”, use 100% testing in the initial stage, and sample according to AQL 2.5 after stabilization
How to deal with the risk of counterfeit components?
Establish a “triple verification” system: XRF detection + supplier audit + blockchain traceability.
What benefits can DFM optimization bring?
Motorola case shows that DFM optimization can reduce manufacturing costs by 18% and shorten production cycle by 30%
What certifications should medical device manufacturers pay special attention to?
ISO 13485 certification must be obtained, and it is recommended to pass MDSAP (Medical Device Single Audit Program) simultaneously to meet multi-national regulatory requirements.
How to quantify the business value of zero defects?
Refer to the “quality cost formula”: TCQ = prevention cost + identification cost + failure cost. A consumer electronics company saves more than $2.4M in annual quality costs through the zero defect plan
Resumen y guía de acción
To achieve zero defect manufacturing, it is necessary to build a full-chain quality system of “design-manufacturing-service”. It is recommended that enterprises proceed in the following steps:
- Diagnose the current situation: Use the [Six Sigma DMAIC]method to evaluate existing processes
- Prioritize improvement: Develop improvement plans for the top 3 defect types
- Technology investment: Plan AOI equipment procurement and PLM system deployment
- Talent development: Cultivate DFM engineers and Six Sigma black belt teams