ما هو اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات (اختبار الدائرة الداخلية) ولماذا اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات؟
اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات هو اختصار لـ "جهاز اختبار الدائرة الداخلية". وهو جهاز اختبار يستخدم تكنولوجيا الحاسوب للتحقق من صحة مكونات ومعامِلات لوحة الدائرة، ومن صحة تجميع الدائرة على خط إنتاج المنتجات الإلكترونية المُنتَج بكميات كبيرة. ولأنه لا يُحاكي وظيفة وأداء دائرة الاختبار، يُطلق عليه أيضًا اسم "الاختبار الثابت للوحة الدائرة".
هو جهاز اختبار يستخدم تكنولوجيا الحاسوب للتحقق من صحة مكونات ومعامِلات لوحة الدوائر الإلكترونية، ودقة تجميع الدوائر في خط إنتاج المنتجات الإلكترونية المُنتَج بكميات كبيرة. ولأنه لا يُحاكي وظيفة وأداء دائرة الاختبار، يُطلق عليه أيضًا اسم "الاختبار الثابت للوحة الدوائر".
اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات جهاز اختبار الدائرة الداخلية (IN CIRCUIT TESTER) يقيس جميع مكونات لوحة الدائرة، بما في ذلك المقاومات والمكثفات والمحاثات والثنائيات والترانزستورات وFETs وSCRs وLEDs والدوائر المتكاملة (ICs)، للكشف عن عيوب مختلفة في منتجات لوحات الدوائر، مثل: قصر الدائرة، الدائرة المفتوحة، الأجزاء المفقودة، الأجزاء الخاطئة، الأجزاء المعيبة أو سوء التجميع، وما إلى ذلك. كما أنه أول من استخدم مرحلات القصب (REED RELAY) التي يمكن تبديلها مئات الملايين من المرات. إنه جهاز اختبار الدائرة الداخلية الذي يتمتع بأعلى تغطية للاختبار، وأكثر الاختبارات استقرارًا، وأكثرها ملاءمة للاستخدام، وأكثرها اكتمالًا في البيانات.
ما هو اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات وكيف يعمل؟
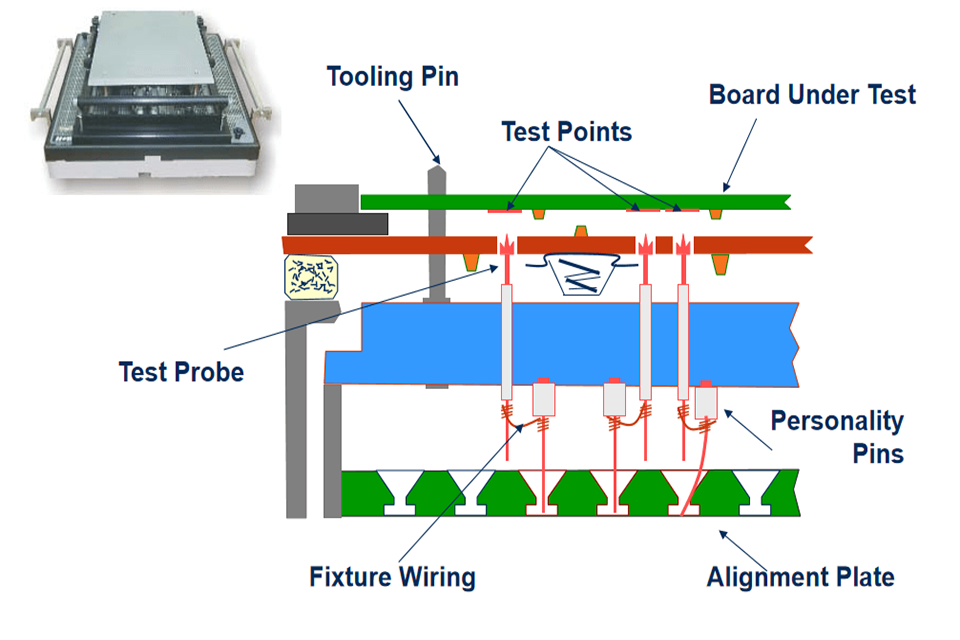
كيف يتم اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات وكيف يتم العمل؟
تقنية العزل (الحراسة) إزالة تداخل الدائرة، وقياس معلمات المكونات بدقة، وتحسين دقة اكتشاف عيوب PCBA.
طريقة قياس التيار/الجهد الثابت تحديد قيمة المقاومة بسرعة، ومناسبة لاختبار المقاومة الكبيرة عبر الإنترنت، لضمان جودة اللحام.
اختبار التردد الثابت للمكثف المتردد قم بقياس معاوقة المكثف من خلال مصدر جهد التيار المتردد، وحدد بدقة سعة المكثف غير الطبيعية (مثل التسرب، واللحام البارد).
طريقة تحليل معاوقة المحث استخدم إشارة التيار المتردد لقياس مفاعلة المحث، وتغطية تشخيص خطأ المحث عالي التردد/منخفض التردد.
اختبار انخفاض الجهد الأمامي للديود اكتشف الجهد الأمامي لثنائيات السيليكون/الجرمانيوم (0.3 فولت/0.7 فولت) للتحقق من الانهيار العكسي أو الدائرة المفتوحة.
اختبار منطق المتجهات مقارنة إشارات الإدخال والإخراج للتحقق من وظائف الدائرة المتكاملة الرقمية (مثل البوابات المنطقية والمعالجات الدقيقة).
اختبار المسح السريع غير المتجه لا يتطلب أي إجراءات معقدة، ويكتشف بسرعة الدوائر المفتوحة والقصيرة في دبوس المكون، ويتكيف مع دوائر SMT عالية الكثافة.
تقنية مسح الحدود (JTAG) كشف الترابط الداخلي للشريحة من خلال سلسلة الاختبار التسلسلية، ودعم موقع الخطأ للأجهزة المعبأة مثل BGA.
ما هي وظيفة اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات؟
ما يلي هو ل اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات 10 وظائف رئيسية
1. كشف الدائرة المفتوحة والقصيرة
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- إلكترونيات السيارات:اكتشاف عيوب اللحام على لوحات دوائر وحدة التحكم الإلكترونية لتجنب فقدان السيطرة على السيارة بسبب الدوائر القصيرة.
- معدات الاتصالات:استكشاف أخطاء الدائرة القصيرة في اللوحات الأم لجهاز التوجيه والمحول وإصلاحها لضمان استقرار نقل الإشارة.
2. قياس معلمات المكونات
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- المعدات الطبية:معايرة معلمات المقاومة والسعة للأجهزة الدقيقة مثل الشاشات وأجهزة التنفس الصناعي وما إلى ذلك، لضمان دقة المعدات.
- التحكم الصناعي:التحقق من أداء المحث والمرحل في PLC (وحدة التحكم المنطقية القابلة للبرمجة) لضمان التشغيل المستقر لخطوط الإنتاج.
- الفضاء الجوي:الفحص الكامل لمعلمات مكونات لوحات الدوائر ذات الموثوقية العالية لتلبية متطلبات الأداء في البيئات القاسية.
3. اختبار الثنائي/الترانزستور
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- وحدة الطاقة:اختبار أداء الصمام الثنائي المعدل وأنبوب التبديل لتجنب ارتفاع درجة الحرارة أو فشل مصدر الطاقة.
- الالكترونيات الاستهلاكية:اختبار الانهيار العكسي للثنائيات في شواحن الهواتف المحمولة ودوائر محرك LED لتحسين عمر المنتج.
- المعدات الصناعية:التحقق من خصائص تضخيم الترانزستور للوحات العاكس ومحرك المحرك لضمان إنتاج طاقة عالية.
4. تقنية العزل (الحراسة)
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- أجهزة قياس عالية الدقة: مثل القياس الدقيق للمقاومة الصغيرة والسعة في دوائر الاستشعار، مما يؤدي إلى القضاء على تداخل الحلقة الطفيلية.
- الفضاء الجوي:اختبار عزل دوائر التحكم الدقيقة لضمان دقة معلمات المكونات الرئيسية في الدوائر المعقدة.
- المعدات الطبية:اختبار الدوائر عالية الحساسية لمعدات تخطيط القلب (ECG) لتقليل أخطاء القياس.
5. تحديد موقع الخطأ تلقائيًا
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- إلكترونيات السيارات:تحديد المكونات المعيبة في وحدات الملاحة داخل السيارة والشبكة داخل السيارة بسرعة لتقصير وقت الإصلاح.
- محطات الاتصالات الأساسية:تحديد دقيق لنقاط خطأ اللوحة الأم لمحطة القاعدة لضمان استمرارية شبكة الاتصالات.
- الأتمتة الصناعية:إصلاح سريع للوحات التحكم الروبوتية المعيبة، مما يقلل من خسائر توقف خط الإنتاج.
6. اختبار الدفعات الفعال
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- الالكترونيات الاستهلاكية:اختبار سريع للوحات الأم للهواتف المحمولة وأجهزة الكمبيوتر على خط الإنتاج، بما يتوافق مع الطلب على إنتاجية SMT عالية (على سبيل المثال، آلاف القطع في الساعة).
- أجهزة إنترنت الأشياء:مراقبة الجودة للدفعات لأجهزة استشعار المنزل الذكي والأجهزة القابلة للارتداء لتحسين كفاءة توصيل السوق.
- التحكم الصناعي:اختبار دفعات من لوحات التحكم PLC واللوحات الأم للتحكم الصناعي لضمان اتساق المعدات الصناعية.
7. تحليل خاص للمكثف والمحث
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- معدات الاتصالات:اختبار معاوقة مكثفات الفلتر والمحثات عالية التردد لضمان جودة الإشارة لمحطات القاعدة 5G.
- الالكترونيات الاستهلاكية:التحقق من أداء مكثفات ضبط هوائي الهاتف المحمول ومحثات ترشيح مصدر الطاقة لتحسين الإشارة والنطاق.
- إلكترونيات السيارات:اختبار استقرار المحاثة لأنظمة الصوت وأنظمة ADAS داخل السيارة لتجنب التداخل الكهرومغناطيسي.
8. اختبار الدوائر المتكاملة
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- إلكترونيات السيارات: اختبار مسح الحدود للرقائق المعبأة في BGA (على سبيل المثال، وحدات التحكم الدقيقة، وأجهزة الاستشعار) لضمان موثوقية أنظمة القيادة الذاتية.
- الفضاء الجوي:اختبار الترابط الداخلي للدوائر المتكاملة المعقدة (مثل FPGA وDSP) لتلبية متطلبات الموثوقية العالية.
9. الإحصاءات والتتبع
سيناريوهات التطبيق:
- الأجهزة الطبية:بيانات إحصائية عن عيوب الأجهزة الطبية لتحسين عمليات الإنتاج للامتثال لمعايير FDA/CE.
- التصنيع الصناعي:تحسين معلمات مثبت SMT ومعدل العائد من خلال اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات التقارير.
ما هي مزايا وعيوب اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات؟
فيما يلي جدول مقارنة لطرق الاختبار الرئيسية الثلاثة اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات، واختبار FCT، وAOI استنادًا إلى معلومات قاعدة المعرفة، مع تسليط الضوء على المزايا والعيوب وسيناريوهات التطبيق
اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات (اختبار الدائرة)
| المزايا | العيوب | سيناريوهات التطبيق النموذجية |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ سرعة الاختبار السريعة (بضعة ثواني/لوحة) | ❌ تكلفة المعدات العالية (مئات الآلاف من الدولارات في التركيبات) | إلكترونيات السيارات، ومعدات الاتصالات، والإنتاج الضخم للإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية |
| ✅ دقة عالية (الاختبار المباشر للخصائص الكهربائية) | ❌ يجب تصميم نقاط الاختبار (معدل توصيل أقل) | لوحات التحكم الصناعية، الدوائر عالية الموثوقية في مجال الطيران والفضاء |
| ✅ دعم للمكونات المعقدة (على سبيل المثال BGA، FPGA) | ❌ متطلبات صيانة عالية (يجب استبدال المجسات في حالة تآكلها) | خطوط PCBA التي تحتاج إلى تحديد الأخطاء بسرعة |
| ✅ لا حاجة لاختبار التشغيل (يقلل من خطر حدوث ماس كهربائي) | ❌ لا يمكن اختبار وظائف البرنامج | لوحات الدوائر الكهربائية عالية الكثافة |
FCT (اختبار وظيفي. اختبار وظيفي)
| المزايا | العيوب | سيناريوهات التطبيق النموذجية |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ التحقق الشامل من الوظائف (التعاون في مجال البرمجيات والأجهزة) | ❌ بيئات الاختبار المعقدة (الحاجة إلى محاكاة ظروف العمل في العالم الحقيقي) | اختبار الهواتف الذكية والأجهزة الطبية والأجهزة النهائية |
| ✅ الاختبار الديناميكي (ظروف العمل الحقيقية) | ❌ يستغرق وقتا طويلا (مستوى الدقيقة/اللوحة) | محطات الاتصالات الأساسية، اختبار تكامل نظام وحدة التحكم الإلكترونية للسيارات |
| ✅ تغطية المناطق العمياء لتكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات (على سبيل المثال، أداء المكونات، عيوب البرمجيات) | ❌ انخفاض الاستثمار في الأجهزة، ولكن تكلفة تطوير البرنامج عالية | الأجهزة المعقدة التي تحتاج إلى التحقق من صحة التفاعلات على مستوى النظام |
| ✅ يمكن تكييفها لإنتاج كميات صغيرة | ❌ غير قادر على تحديد نقاط الفشل المحددة | مرحلة تطوير المنتج الجديد والتحقق منه |
AOI (التفتيش البصري الآلي)
| المزايا | العيوب | سيناريوهات التطبيق النموذجية |
|---|---|---|
| ✅ التفتيش بدون تلامس (لا يوجد تآكل ميكانيكي) | ❌ غير قادر على اكتشاف الخصائص الكهربائية | فحص مظهر وصلة لحام خط SMT، ومراقبة عملية PCB |
| ✅ فحص المظهر عالي الدقة (على سبيل المثال، الجسر الضخم، جسر اللحام) | ❌ يعتمد على التكوينات الخوارزمية ومصدر الضوء | فحص عيوب مظهر الإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية والإلكترونيات الخاصة بالسيارات |
| ✅ ✅ صيانة منخفضة التكلفة (لا حاجة لاستبدال المجس) | ❌ غير قادر على اكتشاف الأخطاء الداخلية | اعتراض العيوب في الوقت الفعلي لخط الإنتاج عالي السرعة |
| ✅ النشر السريع (يتكيف مع التبديل بين النماذج المتعددة) | ❌ متأثر بالتشطيب السطحي (على سبيل المثال، إخفاء المكونات) | إزاحة مكون SMT، الكشف عن طباعة معجون اللحام الضعيف |
ملخص المقارنة والاقتراحات التكميلية
| أبعاد المقارنة | اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات | مقاطعة العاصمة الفيدرالية | هيئة الاستثمار العربية |
|---|---|---|---|
| أنواع الاختبارات | الأداء الكهربائي | الوظيفة | مظهر |
| سرعة | سريع (ثواني) | بطيء (دقائق) | سريع (في الوقت الحقيقي) |
| يكلف | عالية (المعدات + التركيبات) | متوسط (يعتمد على بيئة الاختبار) | الوسيط (المعدات + الخوارزميات) |
| الحلول التكميلية | +AOI (الفحص البصري والكهربائي الكامل) | +ICT (تحديد الأخطاء المحددة) | +ICT/FCT (تغطية الكهرباء والوظائف) |
لماذا نقوم بإجراء اختبار تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات؟
لماذا تختارنا لاختبارات تكنولوجيا المعلومات والاتصالات؟ ——حلول احترافية وفعّالة وموثوقة لاختبار لوحات الدوائر المطبوعة
رابعا، ملخص لمزايانا الأساسية
| أبعاد | نحن نستطيع فعل ذلك |
|---|---|
| كفاءة | وقت اختبار اللوحة الواحدة ≤ 5 ثوانٍ، يدعم أكثر من 2000 نقطة اختبار/لوحة |
| دقة | معدل الإيجابيات الكاذبة < 0.2%، متوافق مع إعداد التسامح ±20% |
| يكلف | توفير تكلفة تركيبات 30%، وتقليل إعادة العمل اليدوي لـ 92% (مشروع المعدات الطبية المرجعي) |
| التغطية التكنولوجية | اختبار المسبار الطائر + اختبار قاعدة المسامير + الكشف عن وصلة اللحام ثلاثية الأبعاد، مناسب للتعبئة عالية الكثافة مثل BGA/LGA/QFN |
| شهادة الصناعة | شهادة ISO 9001/IEC 61215، حالة تعاون SGS/Intertek |