-
Xinxintian Industrial Zone, Shajing Street,Bao'an District, Shenzhen, China

A Beginner’s Guide to Printed Circuit Boards: Understanding the Basics
[ad_1]
A Beginner’s Guide to Printed Circuit Boards: Understanding the Basics
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an essential component of modern electronics, but for those new to electronics, understanding how they work can seem daunting. In this article, we’ll dive into the basics of PCBs, covering what they are, how they’re made, and what they’re used for. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid grasp of the fundamentals and be ready to start exploring the world of PCBs.
What is a Printed Circuit Board?
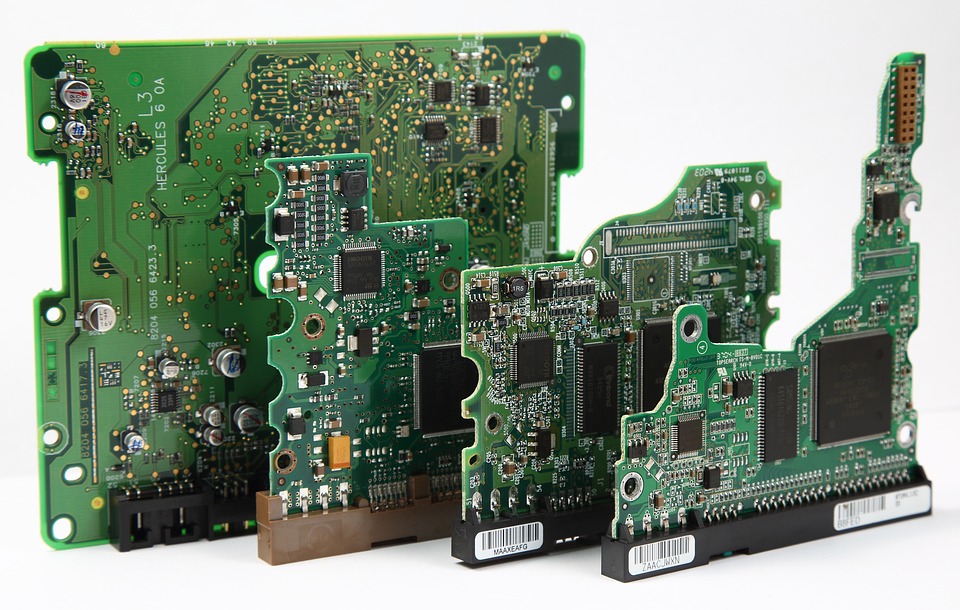
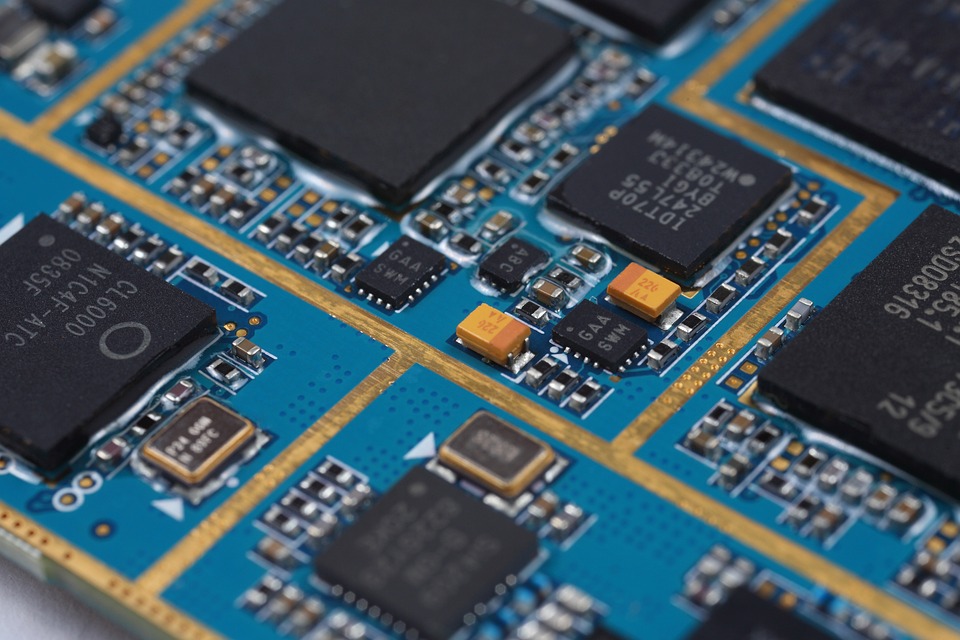
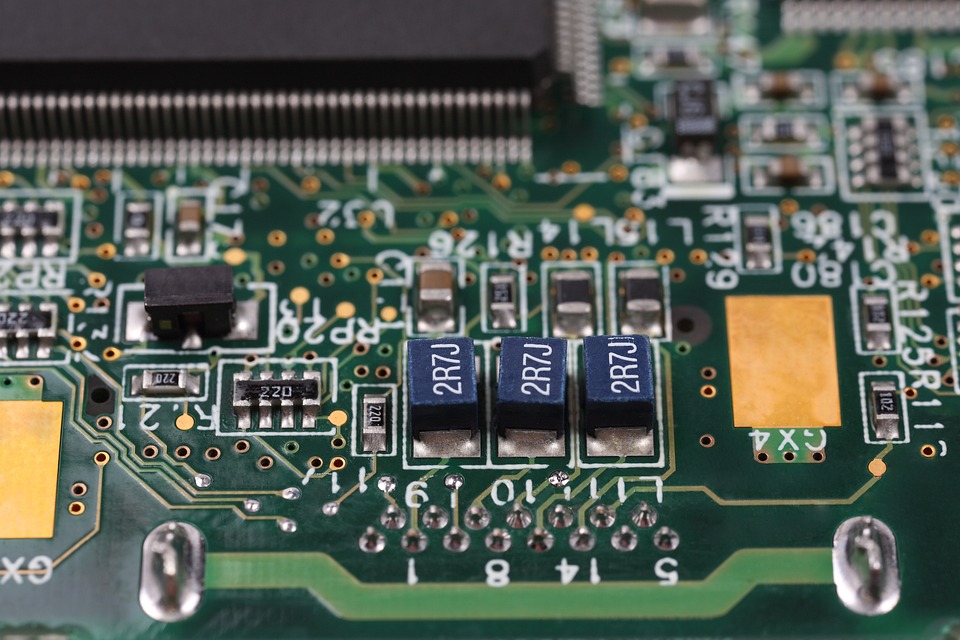
A PCB is a flat, rigid panel made of a variety of materials, such as fiberglass, epoxy, or paper-based materials. It’s used to connect electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs), together to form a circuit. PCBs are designed to provide a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective way to manufacture electronic products, from simple devices like calculators to complex systems like smartphones and computers.
How are PCBs Made?
The process of creating a PCB is a sophisticated one, involving multiple steps:
- Lamination:** The base material, such as a fiberglass or epoxy layer, is coated with a thin layer of insulating material.
- PdN (Photoresist) Application:** A photoresist coating is applied to the base material, typically using a roller or spray.
- Laser or Ultraviolet (UV) Lithography:** A laser or UV light is used to transfer the circuit design onto the PCB. The photoresist reacts to the light, creating a negative image of the design.
- Development:** The photoresist is developed, revealing the positive image of the circuit design.
- Etching:** The unprotected areas of the base material are etched away using a chemical or mechanical process.
- Surface Finishing:** The board is cleaned and coated with a layer of solder mask, which prevents solder bridges and improves reliability.
- Soldering:** The components are attached to the board using soldering techniques, such as wave soldering or reflow soldering.
What are PCBs Used For?
PCBs are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Computer and smartphone manufacturing:** PCBs are used in the production of many electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Routers and switches:** PCBs are used in network devices, such as routers and switches, to enable communication between devices.
- Automotive electronics:** PCBs are used in many automotive applications, such as infotainment systems, navigation systems, and advanced driver assistance systems.
- Medical devices:** PCBs are used in various medical devices, such as MRI machines, ultrasound devices, and pacemakers.
- Aerospace and defense:** PCBs are used in various aerospace and defense applications, such as navigation systems, communication systems, and radar systems.
Conclusion
Printed circuit boards are an essential component of modern electronics, enabling the efficient and cost-effective production of a wide range of electronic devices. Understanding the basics of PCBs is crucial for anyone looking to get started in the field of electronics, and this article has provided a solid foundation. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, the world of PCBs is vast and exciting, with endless possibilities for innovation and discovery.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a PCB and a printed wiring board (PWB)?
A: A PCB is a single-layer board, while a PWB is a multi-layer board with multiple conductive and insulating layers.
Q: What is the best material for a PCB?
A: The best material for a PCB depends on the application, but common materials include FR4 (flame retardant 4), FR3, and FR2 (fluorinated ethylene-propylene).
Q: Can I make my own PCBs at home?
A: Yes, you can make your own PCBs at home using DIY kits or online resources, but it requires a solid understanding of electronics and PCB design principles.
Q: Are PCBs repairable?
A: In some cases, PCBs can be repaired or refurbished, but it depends on the design and complexity of the boards.
Q: Can I use a PCB for a high-power application?
A: It’s generally not recommended to use a PCB for high-power applications, as it can lead to overheating and damage to the components.
Q: Can I use a PCB for a secure application?
A: PCBs can be used for secure applications, such as secure communication systems, but it’s essential to design the board with security features, such as encryption and secure storage, in mind.
[ad_2]